
These findings connect plasticity within the sympathetic nervous system to a physiological output and indicate the strength of the final synapse in this descending pathway plays a decisive role in maintaining euglycemia. Loss of neuropeptide Y prevents a fasting-induced increase in epinephrine release and results in hypoglycemia in vivo. Using genetic and pharmacological approaches we show this plasticity requires neuropeptide Y, an adrenal cotransmitter and the activation of adrenal Y5 receptors. The dominant effect is a presynaptic, long-lasting increase in synaptic strength.
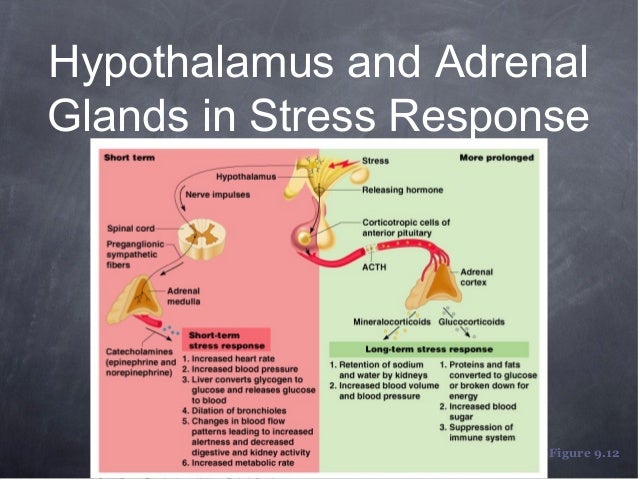
Here we show that fasting leads to altered transmission at the preganglionic → chromaffin cell synapse. However, whether modulation of autonomic function determines the relative strength of the CRR, and thus the ability to withstand food deprivation and maintain euglycemia, is not known. A major effector arm is the autonomic nervous system that controls epinephrine release from adrenal chromaffin cells and, consequently, hepatic glucose production.
During fasting, activation of the counter-regulatory response (CRR) prevents hypoglycemia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
